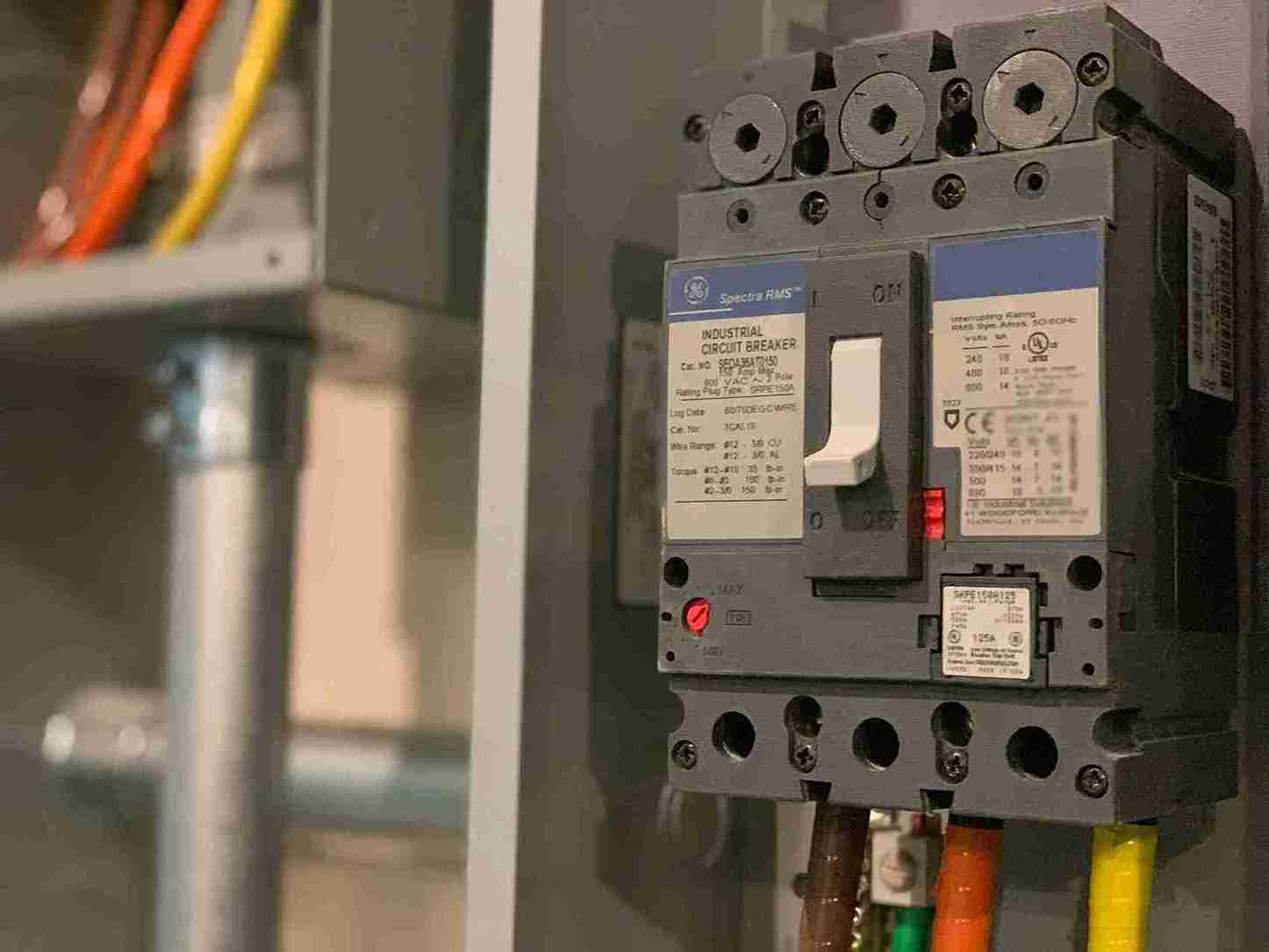
MPCB, also known as Motor Protection Circuit Breaker, and RCCB, which stands for Residual Current Circuit Breaker, are two distinct electrical devices utilized for circuit protection. However, they have distinct functions and offer protection against different types of faults. Below, we will provide a concise overview of the disparities between MPCB and RCCB.
Purpose of MPCB VS RCCB
MPCB (Motor Protection Circuit Breaker)
The main purpose of this device is to safeguard electric motors against overloads, short circuits, and phase failures. It provides specialized protection for motor circuits.
RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker)
The purpose of this device is to safeguard against electrical shocks that may occur due to ground faults or leakage currents. It operates by identifying any disparity between the live and neutral conductors, promptly alerting and isolating the circuit in the event of such imbalances.
Functions of MPCB VS RCCB
MPCB (Motor Protection Circuit Breaker)
The motor’s current is monitored and safeguarded against overcurrent and short circuits. It may also encompass supplementary functionalities like phase failure protection.
RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker)
It oversees the disparity in current between the live and neutral wires, effectively detecting any leakage currents that may arise from human interaction with an electrical device.
Applications of MPCB VS RCCB
MPCB (Motor Protection Circuit Breaker)
MPCB Primarily utilized in motor circuits, such as those dedicated to pumps, compressors, and various industrial machinery.
RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker)
RCCB Utilized in electrical installations for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes, this product serves to augment safety measures against the risk of electric shock.
Operation principle of MPCB VS RCCB
The operational principles of MPCB (Motor Protection Circuit Breaker) and RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker) differ significantly, as they are specifically engineered to tackle various electrical faults. Let’s explore the operational principles of each in detail:
MPCB (Motor Protection Circuit Breaker)
Overload Protection
MPCBs employ a thermal trip mechanism in order to safeguard against overloads. The current passing through the MPCB causes a bimetallic strip to heat up. As the temperature increases, the strip undergoes bending and ultimately triggers the circuit, resulting in the disconnection of the power supply to the motor.
Short Circuit Protection
MPCBs utilize a magnetic trip mechanism in the event of a short circuit. When a high current passes through during a short circuit, a powerful magnetic field is generated. This magnetic force then triggers a mechanism within the MPCB, resulting in the interruption and tripping of the circuit.
Phase Failure Protection
Certain motor protection circuit breakers (MPCBs) are equipped with phase failure protection. These MPCBs diligently oversee the phase sequence and promptly trip the circuit in the event of a phase failure, effectively safeguarding the motor from potential harm.
RCCB (Residual Current Circuit Breaker)
Residual Current Detection
RCCBs are specifically engineered to identify residual currents, which are discrepancies between the live and neutral conductors. The RCCB consistently monitors the current that passes through both the live and neutral wires. In regular circumstances, the currents remain in equilibrium.
Differential Current Transformer
An RCCB utilizes a differential current transformer to identify any disparity in the current flowing through the live and neutral conductors. The presence of any difference signifies the existence of a leakage current, which can arise from electrical faults, such as accidental contact between a person and a live component.
Tripping Mechanism
An RCCB utilizes a differential current transformer to identify any disparity in the current flowing through the live and neutral conductors. The presence of any difference signifies the existence of a leakage current, which can arise from electrical faults, such as accidental contact between a person and a live component.
Disconnection of Power
The RCCB promptly cuts off the power supply upon tripping, ensuring safeguard against electric shock.